You may also like…
He creates you in the wombs of your mothers ˹in stages˺, one development after another, in three layers of darkness.(surah Az-Zumar 39:6)
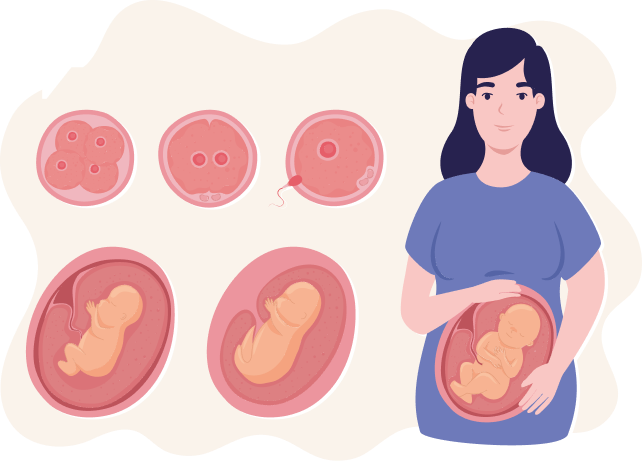
How does a successful pregnancy occur?
In the first week; ovulation (release of the egg) to fertilization (joining of sperm and egg) to implantation (laying down of the joined egg and sperm: blastocyst in uterus) occurs. How does this happen? After sexual intercourse, a million sperms are deposited in the vagina and propel upwards towards the cervix. What is a cervix? It is a part of a female's reproductive system, located at the lowest part of uterus/womb and connects the uterus/womb to the vagina. For a successful pregnancy a man’s sperm must reach the female’s cervix and fertilize the egg. This fertilized egg then further divides waiting to implant or embed in the uterus.
Baby systems development- second and third week
In second and third week of embryology there are three germ cell layers formed within the embryo which give rise to some important structures. These are the ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm.
Blastocyst is a group of cells that are constantly dividing and the inner part of this group of cells which becomes the embryo. When this blastocyst reaches the uterus it anchors itself/implants into the uterus. The outer cells of the blastocyst and the inner lining of uterus help in developing the placenta which is a “cake-like” structure that provides nutrients to the baby and removes toxic substances from the baby.
In the third to eighth week, the ectodermal layer forms central nervous system, peripheral nervous system, sensory epithelium of the ear, nose and eye, skin, hair and nails, pituitary, mammary, and sweat glands, and enamel of the teeth.
The mesodermal layer forms muscle tissue, cartilage and bone, dermis of the skin, which are all supporting cells of the body, the vascular system (heart, arteries, veins, lymph vessels and all blood and lymph cells). Furthermore, it gives the urogenital system which constitutes of the kidneys and reproductive organs and their tubes.
The endodermal cell layer provides the epithelial lining of the gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract and urinary bladder. It also forms the functional parts of the thyroid, liver and pancreas and finally the epithelial lining of the ear cavity and canals.
As a result of the formation of all these systems, the initial flat disc lengthens and forms head and tail regions that cause this embryo to curve into fetal positions. This disc also forms wall folds that grow ventrally and close the body wall.
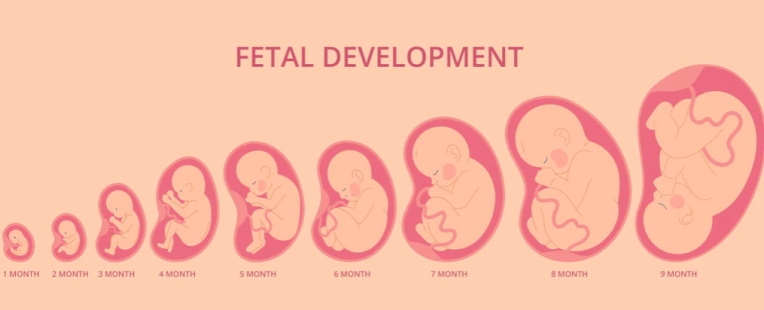
The period from ninth week to birth is called the fetal period. Growth in height of baby is of special importance during the third, fourth, and fifth months while the weight of the baby increases significantly during the last 2 months of pregnancy.
What happens to my baby in the 9 months?
At the beginning of the third month; the head size is about half the size of the body, but over the 9 months, growth of the body speeds up and that of the head slows down.
During the third month, the face transforms into a human-looking countenance. The eyes, which were previously located on the outer side of the face now move inwards and the ear move to their future position; that is, the side of the baby’s head. The limbs grow a relatively appropriate length while the arms are more developed than the legs. By the end of the third month, the bones have developed internally and genitals have developed to the point of identity. This can be detected by an ultrasound. In addition, the gastrointestinal tract/digestive system loops are present within the abdominal cavity and the baby has some reflexed/muscular activity present.
Developmental Horizons during Fetal Life Event.
During the fourth and fifth month, the fetus grows in length quickly and halfway through the pregnancy its head to bottom height at 4.5 months is about 15 cm. The weight of the fetus does not grow a lot during these months and even at the end of the 5th month it is less than 500g. At this point the fetus is covered in special fine hair called lanugo, eyebrows, hair and ears are also visible. During the fifth month, the mother can feel the fetus’ movements known as Braxton Hicks contractions.
During the second half of pregnancy, weight increases drastically, especially during the last 2.5 months (seventh,eighth,ninth month) when half of the final weight is being added (approximately 3200g). In the sixth month, the skin of the fetus is pinkish and is wrinkled due to less percentage of connective tissue and a fetus born during this stage has very little chance of surviving. This is because even though several organ systems are already functioning; the respiratory and cardiovascular systems are not specialized to support life. By sixth to seventh months, the fetus has a height of about 25 cm and is 1100 g heavy. If born at this time, the baby has a 90% chance of surviving.
During the eighth and ninth month the fetus obtains well-rounded curves due to the deposition of subcutaneous (under the skin) fat. At the end of the ninth month, the skulls has the largest all-round size when compared to all the parts of the baby’s body, this is important for normal labour to occur through the birth canal.
At the time of birth, the weight of the baby is about 3000-4000g and length of baby standing is about 50 cm.
O humanity! If you are in doubt about the Resurrection, then ˹know that˺ We did create you1 from dust, then from a sperm-drop,2 then ˹developed you into˺ a clinging clot ˹of blood˺,3 then a lump of flesh4—fully formed or unformed5—in order to demonstrate ˹Our power˺ to you. ˹Then˺ We settle whatever ˹embryo˺ We will in the womb for an appointed term, then bring you forth as infants, so that you may reach your prime. (surah al-hajj, verse 5)
Powered by Froala Editor