You may also like…
Treatment/ Management of Hypertension
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a condition that often requires ongoing management to reduce the risk of complications. Treatment approaches may vary based on the severity of the condition and individual patient factors, but here is a general overview of the treatment and management of hypertension:
Dietary Changes: Adopt a heart-healthy diet that's low in sodium (salt), saturated and trans fats, and cholesterol. Emphasize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and foods rich in potassium.
Weight Management: Achieve and maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular physical activity.
Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling, for at least 150 minutes per week, as recommended by your healthcare provider.
Quit Smoking: Smoking contributes to high blood pressure and increases the risk of heart disease; quitting smoking is essential.
Medications: If lifestyle changes alone are insufficient to control blood pressure, healthcare providers may prescribe medications.
There are several classes of antihypertensive drugs available, including diuretics, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), calcium channel blockers, and others. The choice of medication(s) depends on various factors, including the patient's age, other medical conditions, and potential side effects.
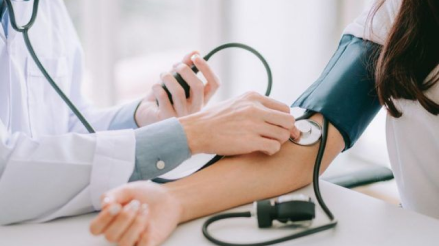
Regular Monitoring: It's crucial to monitor blood pressure regularly, either at home with a home blood pressure monitor or at your healthcare provider's office. Keep a record of your blood pressure readings to track your progress and share them with your healthcare team.
Compliance and Adherence: Take prescribed medications as directed by your healthcare provider, even if you feel fine. Consistency in taking medications is essential for effective blood pressure control.
Regular Follow-up: Visit your healthcare provider for regular check-ups and follow-up appointments to assess your blood pressure and make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
Stress Management: Practice stress-reduction techniques like deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or mindfulness to help lower stress levels, which can contribute to elevated blood pressure.
Management of Underlying Conditions: If you have other medical conditions such as diabetes or high cholesterol, managing these conditions effectively is crucial, as they can exacerbate hypertension.
Dietary Supplements: Some individuals may benefit from dietary supplements like potassium or magnesium, but these should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Powered by Froala Editor