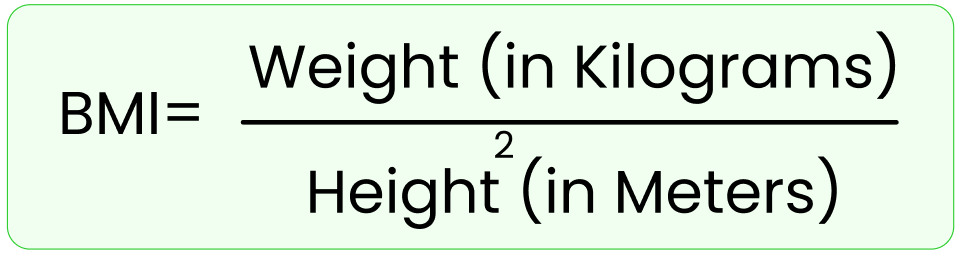You may also like…
What is BMI and How is it calculated?
BMI stands for Body Mass Index, and it is a numerical value that is used to assess whether an individual has a healthy body weight in relation to their height. BMI is a simple and widely used tool for categorizing individuals into different weight categories, such as underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese. Although BMI is often considered an indicator of body fatness, it is a surrogate measure of body fat because it measures excess weight rather than excess fat. It is used for screening health risks, population health studies, treatment planning, health education and resource allocation. It is calculated using the following formula:
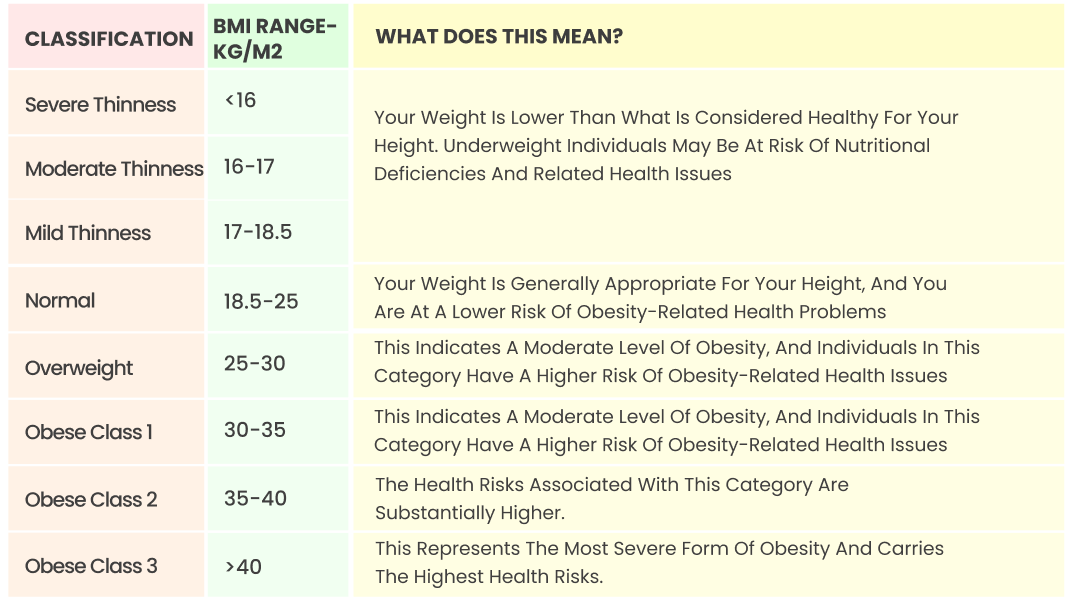
BMI Table for Adults:
This is the World Health Organization’s (WHO) recommended body weight based on BMI values for adults. It is used for both men and women, aged 20 or older. Although some debate continues about whether different categories should exist for specific subgroups (such as Asians), these BMI categories are used worldwide for all adults 20 years and older.
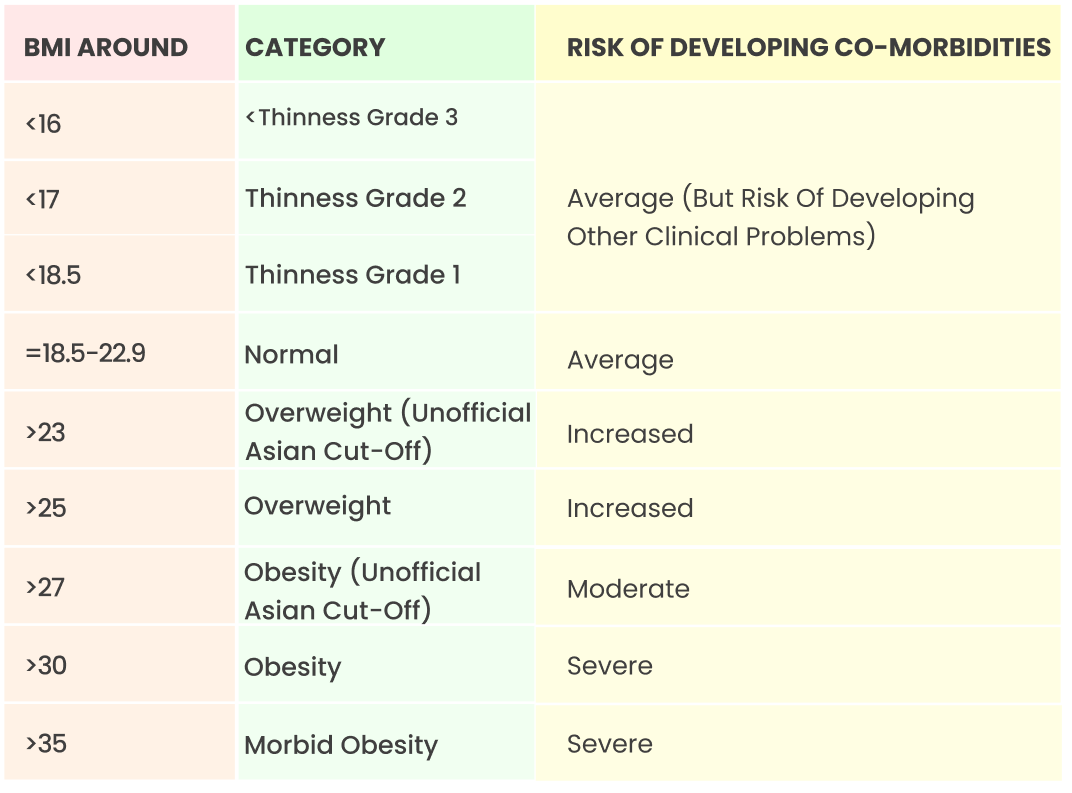
Extended International Body Mass Index Cut-offs for Asian Body type:
These categories are not specific to any particular region or country. They are used as a global standard for assessing weight-related health risks.
However, it is important to note that while the categories may be the same. What is different is how they are interpreted, their management which may depend on various factors including various cultural norms, genetic predisposition, and healthcare practices which vary in different regions of the world.